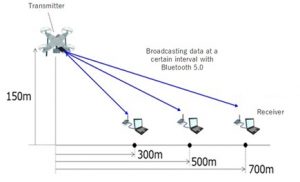
Japan’s New Energy and Industrial Technology Development Organisation (NEDO) government agency reports it has recorded a 95% success rate in evaluating Bluetooth 5.0 for remote identification of drones. A prototype small transmitter was mounted on a drone for the communication evaluation test, flying at an altitude of approximately 150m, and the reception status was evaluated while changing conditions such as the horizontal distance to the evaluation receiver located on the ground.
According to a report on the evaluation: “NEDO has succeeded in evaluating the test of broadcast communication systems to identify drones remotely for the safe and secure operation of drones and other unmanned aircraft. The test was conducted from October 19 to 23 (2020) in the Fukushima Robot Test Field (Namie-cho, Minamisoma-shi, Fukushima) to confirm that it can be identified with a horizontal distance of 300m or more. Specifically, we applied broadcast-type communication evaluation test methods using Bluetooth 5.0 to conduct tests to confirm the success rate of communication between a drone flying at an altitude of approximately 150m with a prototype transmitter and a prototype evaluation receiver located on the ground, and confirmed the performance of a maximum communication success rate of 95% at a horizontal distance of 300m. In this test, we demonstrated the effectiveness of broadcast communication, which is one of the communication systems. In the future, based on this test method, security will be implemented with a view to inspecting and operating the transmitted data, and research and development will be conducted to ensure safe and secure operation of the drone.”
These results are one of the final projects in Japan’s USD128.5 million Drones and Robots for Ecologically Sustainable Societies (DRESS) programme, which has run from financial year 2017 to 2020, under the sponsorship of NEDO. The main research areas in this programme have been:
- R&D of performance evaluation methods – Establish performance evaluation methods for each sector and establish performance evaluation methods for each sector and robot type, for various types of robots (including drones, land-based robots and underwater robots).
- R&D to improve energy-saving performance, etc.- Develop technology for efficient energy systems required for increasing the continuous operating time of various robots.
- Development of drone traffic management systems – Develop various functions and systems to ensure that unmanned aircraft can be operated safely, based on the project’s traffic management systems comprised of information provision functions, flight control functions and integrated traffic management functions.
- Development of drone collision avoidance technology – Develop technology that enables drones to detect objects and other items on land and in the air, so that they can fly by avoiding collisions with those objects in real time.
- De jure standards – Conduct research and development while cooperating on an international level to identify trends among international organizations promoting standardization and various groups in other countries and implement activities for linking the achievements of this project to international standards.
- De facto standards – Gather worldwide latest trend of technology in Japan and promote methods to speed up the development competition based on rules from Japan, regarding robots whose property is that its technological development is extremely fast and de fact standards are the key.
- Evaluating social acceptability with the aim of utilizing the Robot Performance Evaluation Method and the Fukushima Robot Test Field (RTF) for many domestic and overseas robot manufacturers and users, the project managers aim to improve social recognition of robot performance evaluation methods, secure social acceptability regarding concrete performance evaluation methods including standard test methods utilizing various RTF facilities, create concepts such as product out and market-in for RTF users, and develop human resources capable of exercising knowledge, management, and propose capabilities for creating added value in response to the demands of businesses with respective robot technologies.
For more information
https://nedo-dress.jp/en/