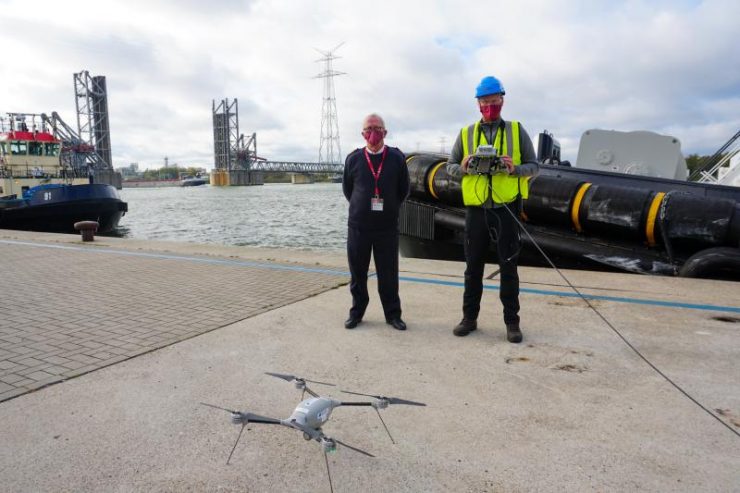
Port authorities in Antwerp, Belgium, are making use of EMSA’s Remotely Piloted Aircraft System (RPAS) to support their day-to-day monitoring of port operations and rapid response to pollution incidents in the port area.
The Belgian authorities requested the service from EMSA following the positive outcome of the SAFIR project led by the SESAR Joint Undertaking for research and development activities in the area of Air Traffic Management. Through this project, the Port of Antwerp was able to test the feasibility of using drones to monitor their port activities.
Taking this forward, the Port of Antwerp in cooperation with Belgium’s Federal Public Service (FPS) for Mobility and Transport entered into an agreement with EMSA for the provision of RPAS services. The operation which has been running since the beginning of October continues until the end of the year and is the first time EMSA has provided RPAS services for the purpose of port monitoring.
The specific RPAS being employed is the Indago quadcopter operated by a pilot from EMSA’s contractor, Nordic Unmanned. The focus is on using unmanned technology to help port authorities conduct safe and efficient surveillance of ship and port operations as well as to respond to safety and pollution incidents rapidly. The flights are streamed live to EMSA’s RPAS Data Centre where they can be viewed by authorised port users to monitor the situation on the ground and take action as and when it is necessary.
The Port of Antwerp is one of the biggest port areas in the world, with a total port area of 120km2, or about 20.000 football fields. In addition to having a 166km long quay, Port of Antwerp registered over 14.400 seagoing vessels, making the port one of the busiest in the world. The focus is on using unmanned technology to help port authorities conduct safe and efficient surveillance of ship and port operations as well as to respond to safety and pollution incidents rapidly.
(Image: Port of Antwerp)
For more information visit: