The New York Power Authority (NYPA) today approved the first phase of funding for a USD37.2 million Unmanned Aerial System (UAS) drone program to roll out new inspection capabilities over the next five years and position the nation’s largest state utility as an industry leader in robotic initiatives. Formalization and expansion of the program is aimed at improving the safety and efficiency of NYPA’s operations, reducing costs, and advancing NYPA’s role in leading efforts to realize New York’s clean energy future.
The Board of Trustees supported the concept of a five-year implementation plan and authorized an initial USD9.6 million for foundational measures needed to enable current and future advancement capabilities. The USD9.6 million includes costs for equipment, software, personnel, training, procurement, regulatory compliance, and contingency.
Drones and UAS have improved rapidly in recent years and are now essential tools that support the Authority’s operations. Planning for a formal drone program began in 2019 when policies and procedures were developed to guide drone use. In 2021, a drone program manager was hired to create a unified program to help support the Authority’s strategic VISION2030 goals.
Since then, software has been procured and is being implemented to support drone pilots; training has been improved with nearly 100 pilots across the Authority; and equipment is being standardized and procured leading the Authority to have an expanded and advanced drone fleet. The new program will enable consistency across the organization; develop standardized policies and procedures for mission planning and flying; and generate a robust data platform that will allow for easily saving and viewing data that has been generated from drone missions.
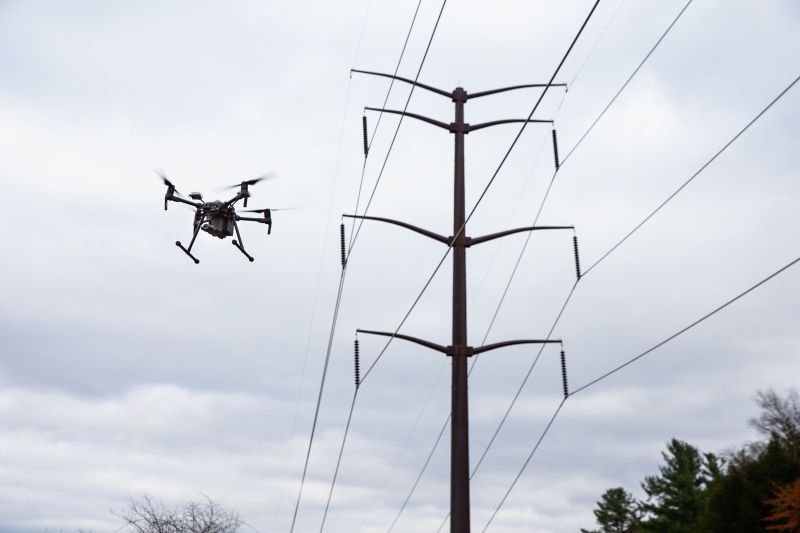
The use of robotics and drones also allows NYPA to minimize exposing personnel to dangerous situations such as climbing transmission poles or being near energized substation equipment. Drone usage also lessens the need for manned helicopter flights to inspect transmission lines. Drones are equipped with high-resolution cameras and sensors that can detect faults and anomalies that may be invisible to the human eye, ensuring potential hazards are identified and addressed before they cause problems.
Earlier this year, NYPA received its first federal approval to fly drones beyond the visual line of sight of the pilot in command. The Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) waiver enables NYPA to conduct fully remote drone operations such as asset and vegetative management inspections at its Blenheim-Gilboa Pumped Storage Power Project in Schoharie County.
For more information visit:
www.nypa.gov